3 min read
4375-4381: A Stuffed Holiday Plan

Earth planning date: Monday, Nov. 25, 2024
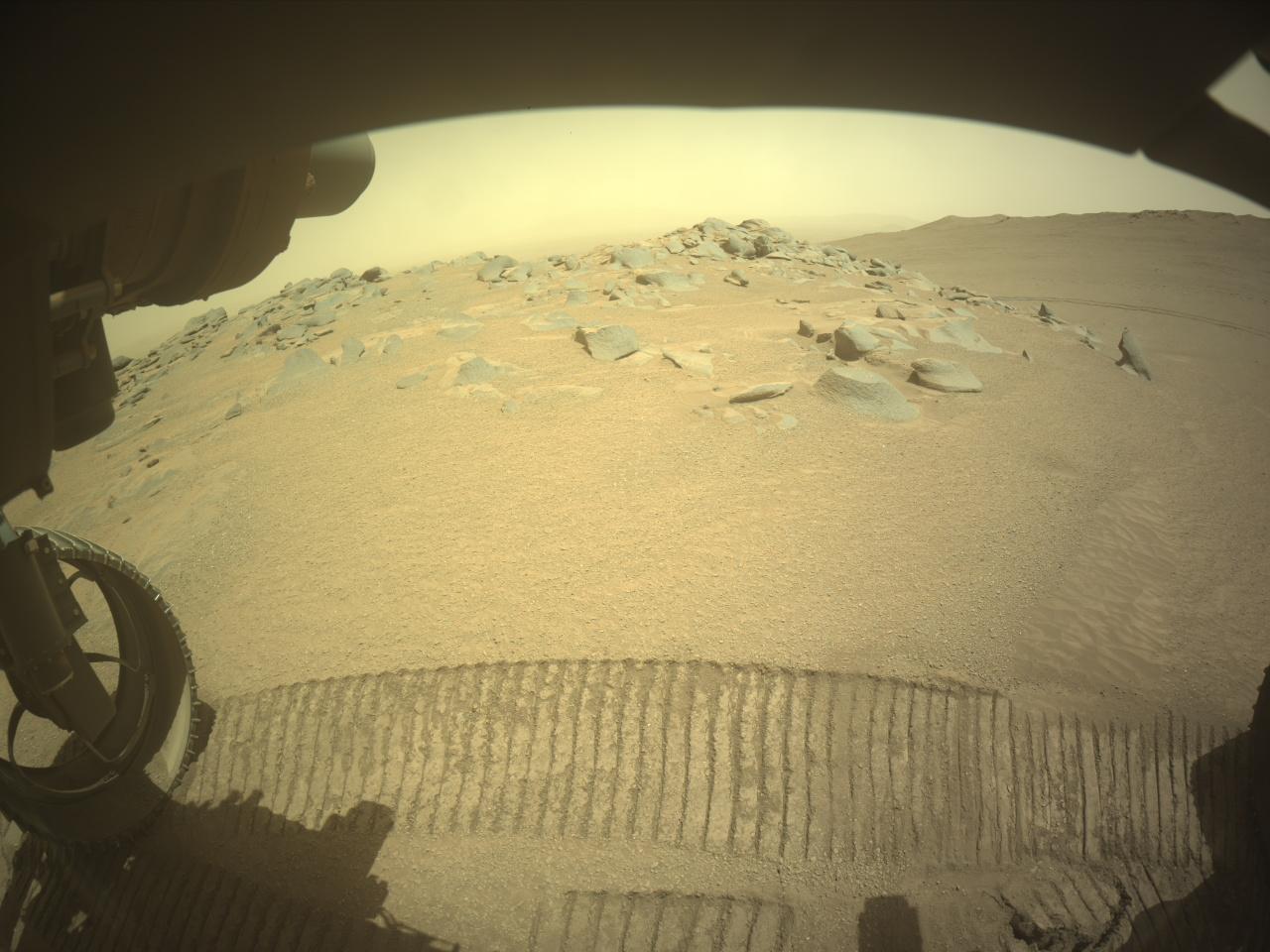
Today we planned a mammoth seven-sol plan, to cover the U.S. Thanksgiving holiday period. Unfortunately, our weekend drive ended a little early and we didn’t receive all of our needed confirmation imagery. At 7 feet high and weighing about 2,000 pounds, the rover itself is as big as a large car (check out this page, with a 3D interactive model of the rover, and more details about its dimensions). However, the contact science instruments are at the end of the arm, which stretches for another 7 feet (2.1 meters) when fully extended — for example, when reaching for a target in the workspace. We really need those confirmation images to be sure that all six wheels are firmly planted on the ground before taking out the arm to do contact science — no one wants our rover to be all wibbly-wobbly, like a giant tower of Thanksgiving jello!
So, no APXS or MAHLI this Thanksgiving; but we have so many other activities, it’s a very stuffed plan. Mastcam has more than five hours of activity across the plan. A planned mosaic of Texoli butte and surrounding area grew so large, it was split into two distinct activities of a 50×4 mosaic (four rows of 50 images) and a 50×1 mosaic.
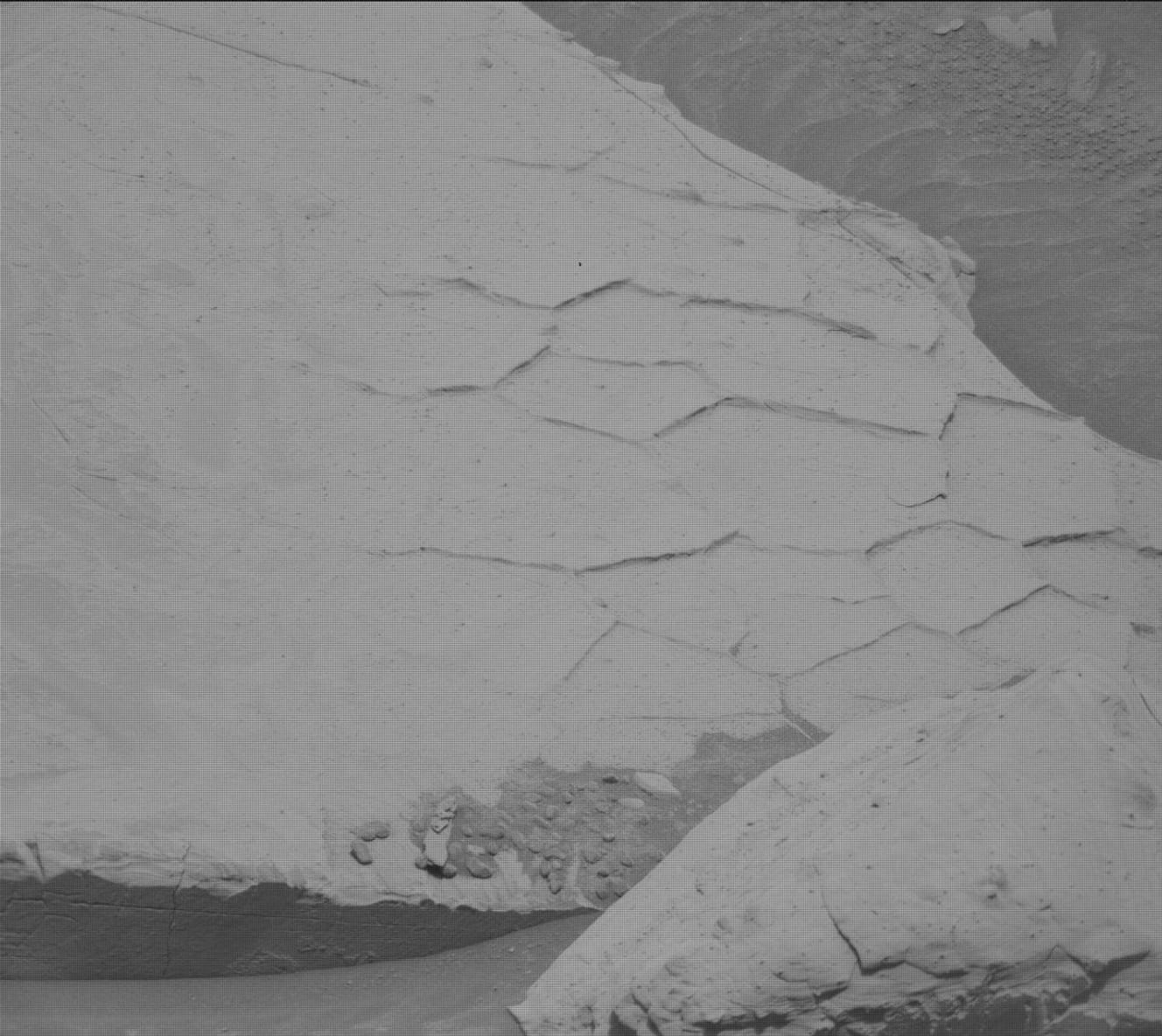
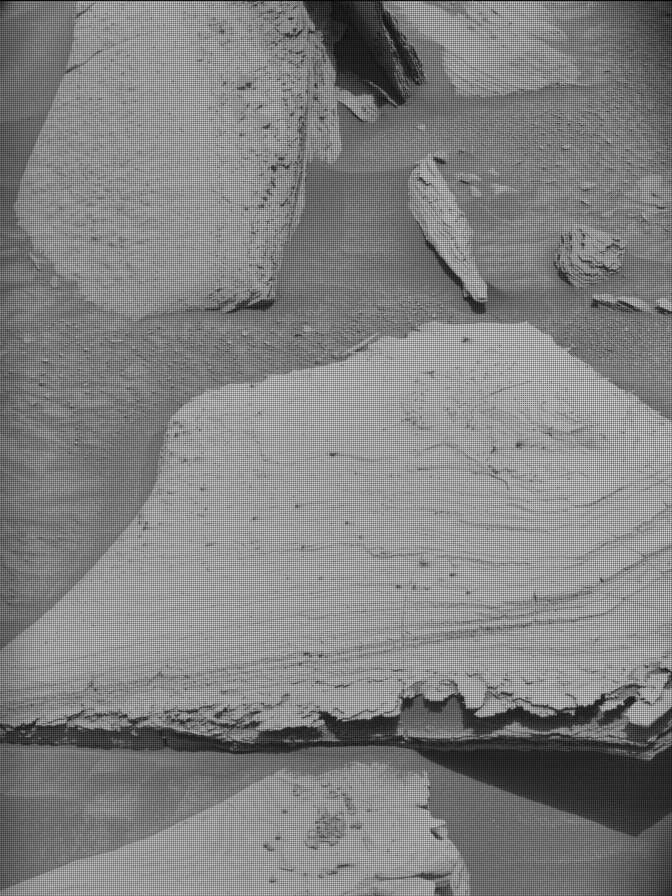
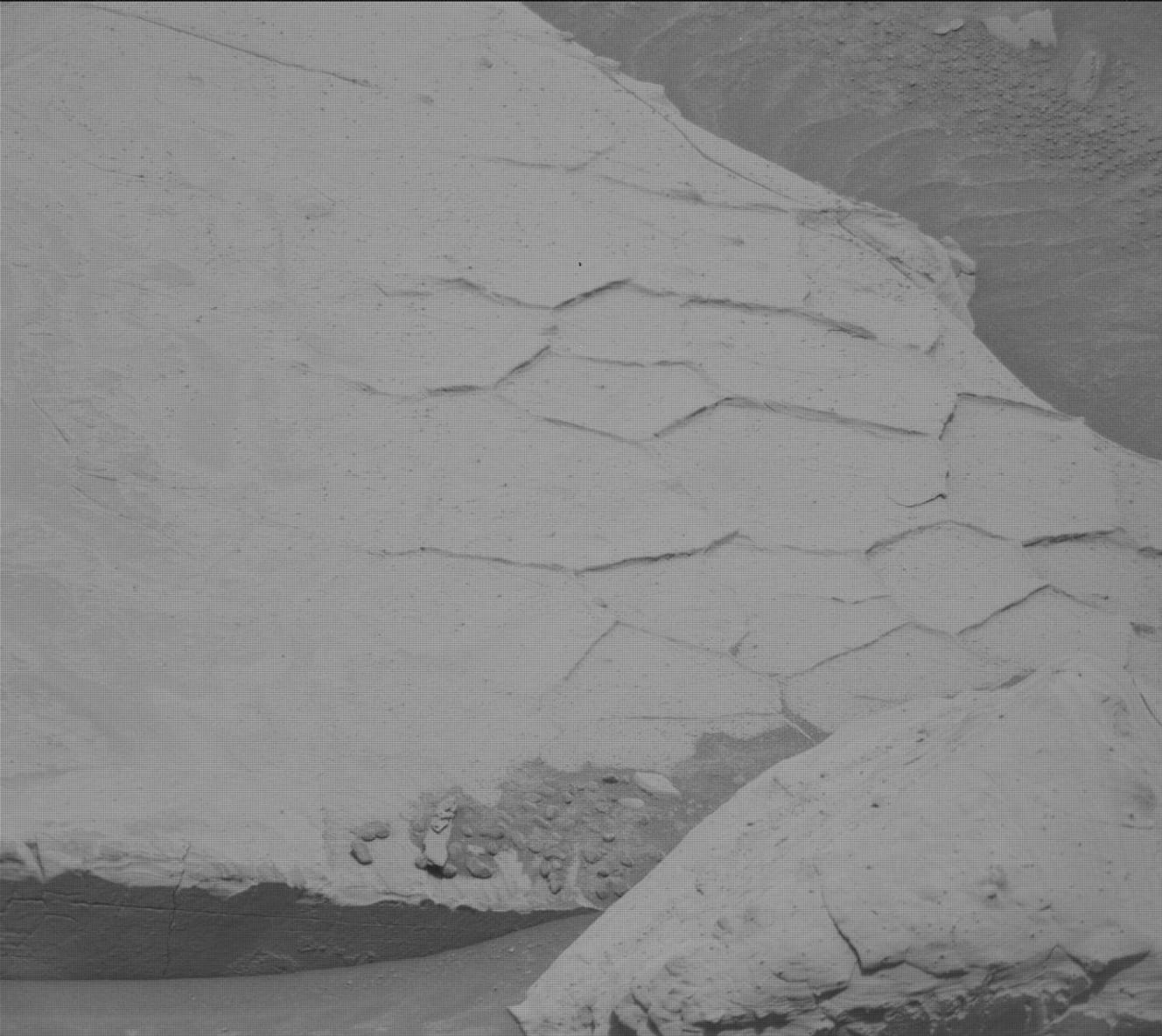
This dusty workspace has so many interesting features, with abundant spherical nodular or concretionary features (typically less than 2 centimeters, or 0.79 inches, in diameter), thin dark-toned layers interbedded with the more dominant paler-colored bedrock and some well-preserved polygonal ridges. Mastcam will image the workspace in a 4×4 mosaic, giving us a lot more information on nodule size and distribution, and on the relative stratigraphic placement of the darker-toned layers, polygonal raised ridges (like those in the accompanying image), and nodules. A second (4×3) mosaic to the right of the rover at “Saurian Crest” looks at variations in bedding layers. ChemCam will take LIBS measurements on some of the larger nodular areas at “Golden Bear Lake” and “Frying Pan Lake” and a further measurement on part of a polygonal ridge at “Caltech Peak.”
The environmental theme group (ENV) will run activities across the plan too. The REMS instrument will acquire data right across the week. A series of single frame change detection Mastcam images on two areas of converging ripples (“Ostrander Hut”) are planned — these will be taken on three different sols to look for changes in the sediment pattern, which could give information on wind movement, strength, and direction. Mastcam will take three “tau” measurements, imaging the sky to quantify the amount of dust in the atmosphere, and Navcam will acquire dust-devil movies and suprahorizon movies on three separate sols.
Our drive on the sixth day of the plan will set us in a new workspace. As one of the NASA engineers said today, we will be looking at “rocks billions of years old, on another planet that has never been looked at before by human eyes” — we have a lot to be grateful for this Thanksgiving holiday!
Written by Catherine O’Connell-Cooper, Planetary Geologist at University of New Brunswick